Structure and Function of the Cervix
The cervix is the lowest part of the womb that connects the womb to the vagina.
It provides a passage between the vagina and the womb, which is very important for reproduction.
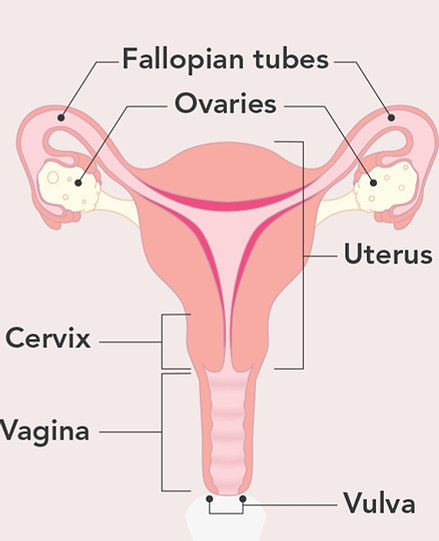
Figure 1: The structure of the cervix
Risk factors for Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer starts in the cells lining the cervix, and specific risk factors of cervical cancer include.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Infection causes about 70% of cervical cancers. It can infect cells on the surface of the skin, genitals, mouth, and throat. HPV can spread from one person to another during sexual or skin-to-skin contact. Different types of HPV cause abnormal growths (warts) on other body parts.
Risk factors for HPV infection, persistence, and development of cervical cancer include.
- Early age at first sexual intercourse
- Multiple sexual partners
- Tobacco use
- Poor ability of the body to fight infections (immunity) e.g. HIV-infected individuals are at higher risk of HPV infection.
- Family history of cervical cancer
- Other STIs, e.g. Chlamydia, Herpes
- Diet low in fruits and vegetables
- Overweight
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
- Change in usual vaginal discharge
- Heavier menstrual bleeding
- Longer menstrual cycle
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Unexplained weight loss
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer can be prevented through screening tests or vaccination.
Screening Tests
Screening tests for cervical cancer help to detect early cancer among women who have no symptoms and may feel healthy. Two main types of screening tests are :
Pap Smear
- The most common test for early changes in the cervix that indicate the presence of cervical cancer.
- A Pap smear should be done every three years for everyone with a cervix from age 25 to 65.
HPV Tests
- HPV Tests should be done alone every five years for everyone with a cervix from age 25 until age 65.
- A combined HPV test and Pap smear can be done every five years for everyone with a cervix from age 30 until age 65.
Vaccination
- The vaccine against HPV protects against new HPV infections
- It is NOT effective against existing HPV infections
- The vaccine should be received by females aged 9-26 years
- Older people can be vaccinated after a discussion with their doctor.
Written and reviewed by
Dr Odiri Oniko (MBBS, GMC-Clinical Fellow)
Dr MaryJane Nweje (MBBS, MSc)
Sources:
- https://www.britannica.com/science/cervix
- https://www.jeanhailes.org.au/resources/uterus-cervix-ovaries-fact-sheet
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cervical-cancer/about/what-is-cervical-cancer.html

